Cloud-based tools for Cerebral Palsy neuroimaging
Tools for interpreting findings from magnetic resonance images (MRI) can support clinical decision making for patients with cerebral palsy (CP).
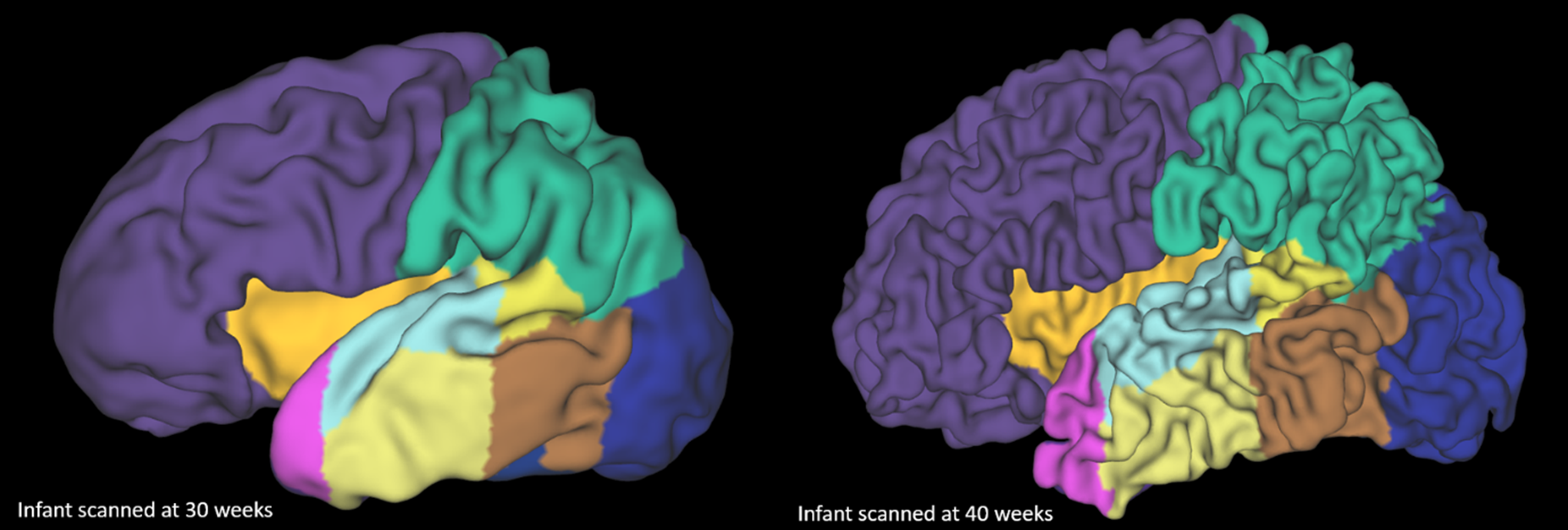
The rapid cortical development of an infant between 30 weeks gestation age (left) and 40 weeks (right).
The challenge
CP is the most common motor disability in childhood, associated with cognitive, behavioural and motor deficits.
Early and accurate identification of CP and implementation of targeted early interventions can be facilitated by MRI. However, current imaging tools are limited by the inability to account for severe image artefacts or pathology.
As such, clinicians use MRIs only in a qualitative fashion. Quantitative measures, which could provide predictive biomarkers, are not currently used.
Our response
We are developing a suite of algorithms that quantify brain structure and microstructure from MRIs. The software tools are robust to severe brain injury and motion artefacts.
Our approach enables the quantitative characterisation of brain structure (e.g. cortical morphology). This allows for increased understanding of biomarkers of brain structure and can contribute to the prediction of patient outcomes. Overall, our algorithms facilitate accurate prognosis from MRI.
Benefits
Our tools have been used to characterise the microstructural properties of the neonatal brain. They have also been used to identify biomarkers to predict developmental delay and neurodevelopmental outcome.
We’ve delivered these tools via MILXcloud for research and clinical collaborators to access.
We’re currently investigating the utility and implementation of the tools for clinical reporting. This includes outlining the biomarkers derived from prediction models and providing estimates of patient outcomes to support decision making around patient-tailored treatments.
The Australian e-Health Research Centre (AEHRC) is CSIRO's digital health research program and a joint venture between CSIRO and the Queensland Government. The AEHRC works with state and federal health agencies, clinical research groups and health businesses around Australia.
