sVEP – accelerating variant annotation and curation

We’ve created a highly scalable cloud-native annotation framework for genomic variants that enables rapid turnaround for clinical tests.
The challenge
An individual’s genome can inform diagnostic and treatment choices. However, prioritising the actionable variants amongst the patient’s millions of genetic mutations is resource intensive.
Annotating a whole genome with clinical information and known functionalities is currently as time-consuming as reading the genome itself. This severely lengthens turnaround times for clinical tests.
Furthermore, with genomic information used in a wide range of application domains, relevant annotation sources can vary dramatically. This requires a highly flexible framework able to focus on the relevant information.
Our response
In collaboration with Pathology Queensland and QIMR Berghofer, we have created a fully cloud-native architecture that enables the rapid and flexible annotation of genomic variants.
Utilising AWS function compute, sVEP is a fully serverless framework that can be automatically deployed in a user’s cloud-account.
The framework can run over patient-individual VCF files or large cohort VCF files.
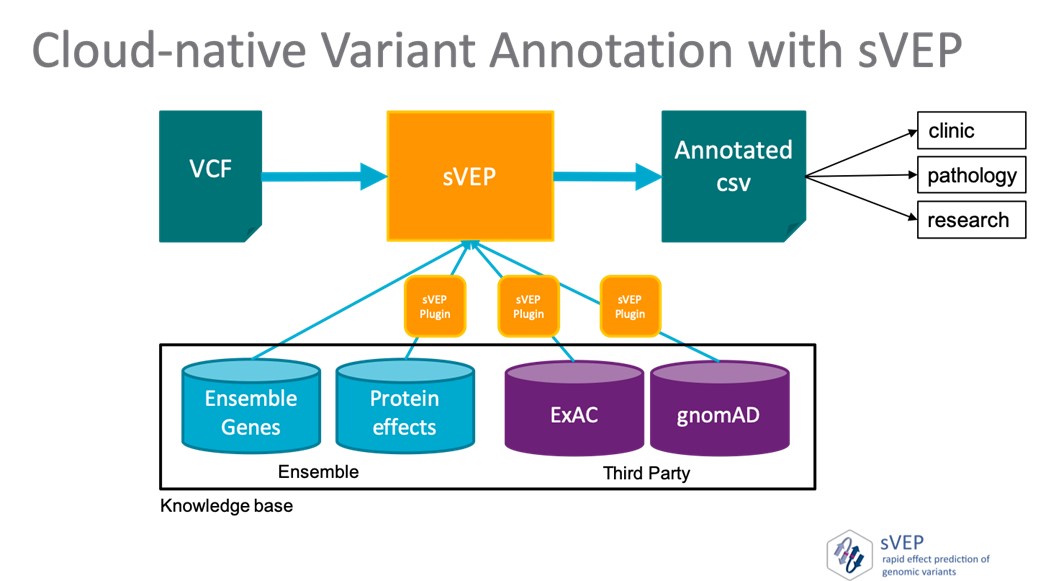
The framework has an orchestration engine that allows the selective execution of provided and external annotations plugins, making workflows highly customisable.
Benefits
Serverless VEP is estimated to be 98% faster than traditional VEP implementations as it can massively-parallelise the annotation task.
When not queried, the cloud set-up does not incur cost, making it sustainable for small pathology laboratories or research institutes.
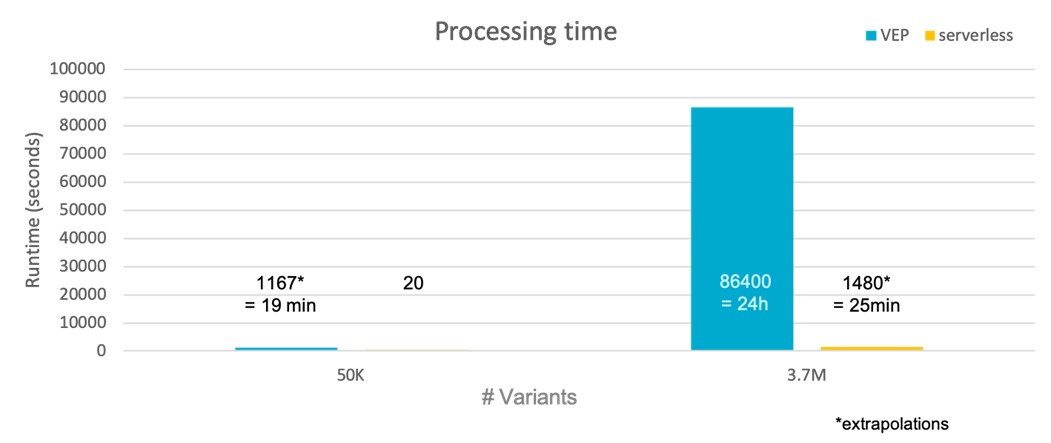
Faster processing times are delivered by sVEP
The Australian e-Health Research Centre (AEHRC) is CSIRO's digital health research program and a joint venture between CSIRO and the Queensland Government. The AEHRC works with state and federal health agencies, clinical research groups and health businesses around Australia.
